We all know that engine oil is the most important lubricant in your vehicle. Engine oil is used to lubricate internal engine parts which are in constant friction. With time, engine oil is being consumed by some parts and it gets very dirty. It is then very important to have regular services done and to replace the engine oil.
When a vehicle’s oil level continues to drop, it is most likely that there is an oil consumption issue in the engine. Many vehicle owners complain about oil consumption, but there are no obvious oil leaks. But when do you know if your vehicle is using too much oil? What calculations can be done in order to determine if the engine is not burning oil?
Understanding the term ‘Burning oil’

When the engine is ‘burning oil’, it simply means that older engine parts allow the oil to escape into the combustion chamber. When the engine is burning oil, the first indication might be a low oil level and blueish smoke coming from the exhaust.
To solve this issue, some internal engine components might need replacement, such as the timing covers and gaskets, valves, rear main oil seal and other seals and gaskets.
Here are a few reasons why your vehicle would consume too much oil:
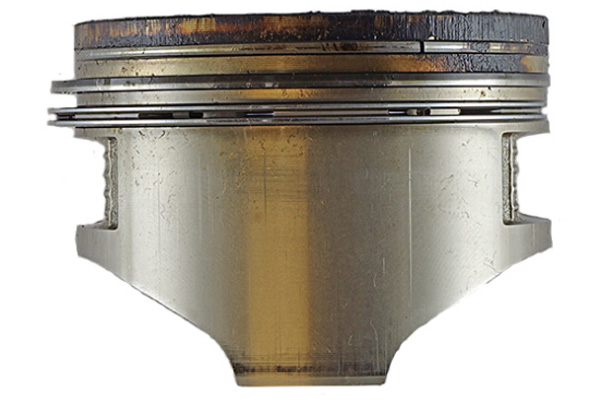
1. Worn piston rings
Pistons move up and down in the cylinders of the cylinder head. The pistons need sufficient lubrication to do so. A piston consist of three rings, namely the wiper ring, compression ring and oil ring.
The oil rings control the amount of oil to lubricate the cylinder walls where the pistons move up and down. When the engine oil is dirty and contains soot, it can damage or wear the piston oil rings. This causes oil to push excessively through the piston rings, causing a loss in engine oil. When pistons rings collapse, there will sometimes be white smoke coming from the exhaust to indicate that there is excessive oil in the cylinders.


2. Leaking head gasket
The cylinder head gasket’s main function is to seal the combustion chamber of the engine so that the vehicle can build up the right amount of compression to maintain engine power. The cylinder head gasket also seals oil galleries in the engine block and head, allowing circulation of oil. If the head gasket leaks, it can dump oil directly into the cylinders, causing the oil to get burnt. When a vehicle overheats, it might cause damage to the head gasket. This will cause oil to leak into the cylinders and a loss of compression. The driver will immediately feel a loss on power and also notice white smoke coming from the exhaust.
3. Bad valve stem seals
Intake valves allows an air mixture into the cylinder head, while the exhaust valves help gasses to escape the engine. The valves are situated in the cylinder head and are designed to open and close at certain times. Valve stem seals form part of the valves and their function is to provide the correct amount of oil needed to lubricate the vales for the movement. Valve stem seals can wear out with time due to the constant friction. This will cause excessive oil to push through the stem seals and release it in the cylinders, causing oil to burn.


4. Oil in coolant system
When your vehicle is consuming oil but there are no leaks, it is also possible that oil ends up in the coolant system. The first sign that there is oil in the coolant system will be noticeable in the coolant. When the coolant in the bottle has an oily appearance, this indicates a coolant and oil mixture. There are a few reasons why this might happen.
The most common reason for oil and coolant mixture is a blown head gasket. The next reason, can be a faulty oil cooler. The oil cooler’s function is to cool down the engine oil to prevent overheating. Sometimes a seal or gasket in the cooler can fail, causing oil and coolant to mix. Lastly, a crack in the cylinder head might also cause a coolant and oil mixture.
5. Turbo issues
Oil flow through the turbo to lubricate internal parts and bearings. Turbo seals might leak oil into boost pipes, causing it to escape. This causes oil to then end up in the exhaust system, and again, causing excessive smoke and oil to get burnt.

What happens when your car runs low on engine oil?
Ever heard of the term ‘your engine has seized up’? Well, that is basically what happens when your vehicle runs out of engine oil. We know that engine oil is supposed to lubricate internal components, and without this lubrication, components will grind each other down instead of sliding against each other smoothly. When a low oil level is noticed too late, this might cause severe and permanent damage to the engine and internal components.
How do I know the oil level is low?
In newer vehicles, there are more diagnostic tools that will indicate a low oil situation. This includes an oil level sensor and oil level warning light on the dashboard. Owning an older vehicle means that drivers have to manually check the oil level with the dip stick.
Oil maintenance on older vehicles
Vehicle maintenance and regular servicing can contribute to the life span of the vehicle. When the vehicle is older, it is wise to use thicker engine oil and to decrease service intervals from 15 000km to 10 000km.
Be wise and prevent bigger damage. Should you notice that your engine’s oil level is low or the warning appears, make sure to take your vehicle to the nearest VAG Spec Centre.








